Description
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), a collaboration between the
National Cancer Institute (NCI)
and
National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), has generated comprehensive,
multi-dimensional maps of the key genomic changes in 33 types of cancer. The TCGA
dataset, 2.5 petabytes of data describing tumor tissue and matched normal tissues from
more than 11,000 patients, is publically available and has been used widely by the
research community.
The Cancer Genome Atlas is a NIH-funded project to catalog genetic mutations
responsible for cancer. The data shown here is RNA-seq expression data produced by the
consortium.
For questions or feedback on the data, please contact
TCGA.
TCGA Gene Expression
The gene track shows RNA expression level for each TCGA tissue in GENCODE canonical
genes. The gene scores are a total of all transcripts in that gene.
TCGA Transcript Expression
The transcript track shows RNA expression levels for each TCGA tissue using GENCODE v23
transcripts.
Display Conventions
In Full and Pack display modes, expression for each genomic item (gene/transcript) is
represented by a colored bar chart, where the height of each bar represents the median
expression level across all samples for a tissue, and the bar color indicates the
tissue.
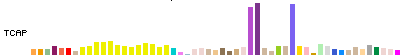
The bar chart display has the same width and tissue order for all genomic items.
Mouse hover over a bar will show the tissue and median expression levels.
The Squish display mode draws a rectangle for each gene, colored to indicate the tissue
with highest expression level if it contributes more than 10% to the overall expression
(and colored black if no tissue predominates).
In Dense mode, the darkness of the grayscale rectangle displayed for the gene reflects the total
median expression level across all tissues.
This track was designed to be used in conjunction with the GTEx expression tracks that can act as a
control.
The color of each cancer was derived by mapping the tissue of origin to the closest GTEx tissue,
then taking the GTEx tissue's color. Five cancers did not have a matching GTEx tissue and were
assigned a rainbow color scheme; these cancers are Cholangiocarcinoma, Esophageal carcinoma, Head
and Neck squamous cell carcinoma, Sarcoma and Uveal Melanoma.
The ordering of the cancers is based on the alphabetical ordering of their GTEx tissues. The five
cancers that did not match were ordered alphabetically.
Methods
TCGA chose cancers for study based on two broad criteria; poor prognosis/overall
public health impact and availability of human tumor and matched normal tissue samples that meet
TCGA
standards.
RNA sequencing was performed using a polyA library and the Illumina HiSeq 2000 platform. All RNA
sequencing was performed by UNC.
Sequence reads for this track were quantified to the hg38/GRCh38 human genome using kallisto
assisted by the GENCODE v23 transcriptome definition. Read quantification was performed at UCSC by
the Computational Genomics lab, using the
Toil
pipeline. The resulting kallisto files were combined to generate a transcript per million (tpm)
expression matrix using the UCSC tool, kallistoToMatrix. By totaling the TPM values for all
transcripts associated to the canonical transcript/gene, a condensed gene per million (gpm) matrix
was made. For both matrices average expression values for each tissue were calculated and used to
generate a bed6+5 file that is the base of each track. This was done using the UCSC tool,
expMatrixToBarchartBed. The bed track was then converted to a bigBed file using the UCSC
tool, bedToBigBed.
Credits
Data shown here are in whole based upon data generated by the
TCGA Research Network.
John Vivian, Melissa Cline, and Benedict Paten of the UCSC Computational Genomics lab were
responsible for the sequence read quantification used to produce this track. Chris Eisenhart
and Kate Rosenbloom of the UCSC Genome Browser group were responsible for data file
post-processing, track configuration and display type.
References
J. Vivian et al.,
Rapid and efficient analysis of 20,000 RNA-seq samples with Toil
bioRxiv bioRxiv, vol. 2, p. 62497, 2016.
|